Many materials are allowable to be used as ultra/micro filtration membrane, such as:
- inorganic materials
- ceramic
- metal
- carbon and organic material…
Available materials are:
- polysulfone (PS)
- polyethersulfone (PES)
- polyacrylonitrile (PAN)
- polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)
- polypropylene (PP)
Each kind of material has its own feature, and is suitable for different working condition. The product performance is decided by material modification and different manufacture process level.
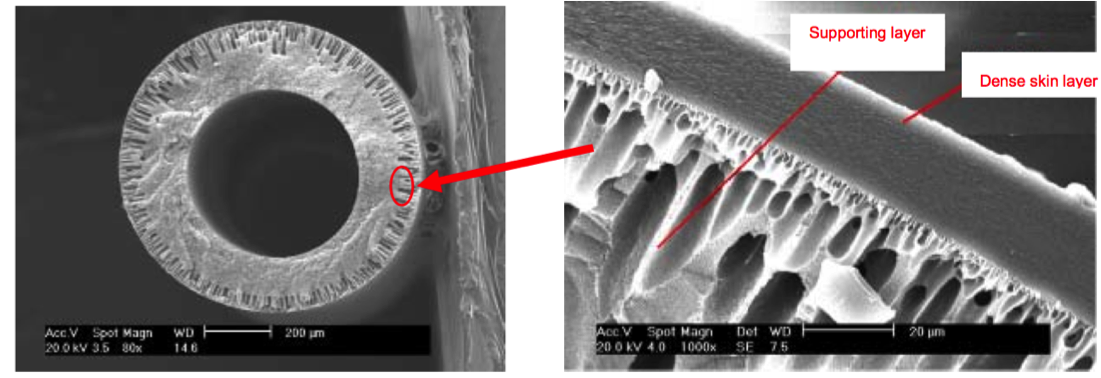
Figure 1. Micro structure of membrane fiber
The advantages of PVDF compared with other membrane materials
Nowadays, the common hollow fiber membrane materials in the market are PS, PVC, PES and PVDF.
Among these materials, PVDF can be used in many fields like tap water purification, water reuse, industrial waste water treatment etc. with great adaptation. See table 1.1 for specific performance of the different materials.
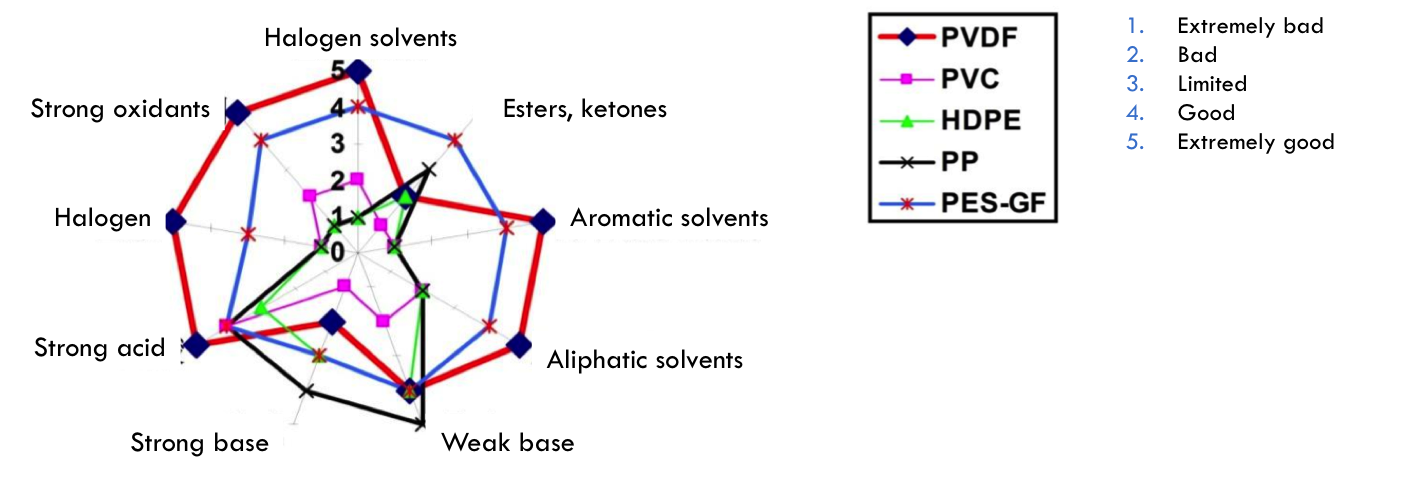
PVDF is globally recognized as the best membrane material with excellent chemical stability, best anti-pollution and oxidative resistance. See figure 1.2 for comparison of the stability of the different materials in different agents.
Table 1.1: Performance comparison table of membrane materials
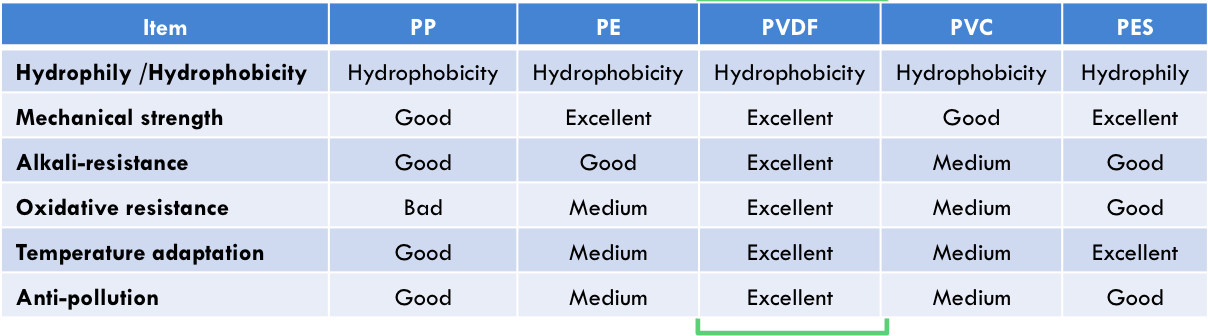
Figure 1.2: Stability of the different materials
Performance of PVDF
PVDF is one kind of semi-crystalline polymer with density of 1.75~1.78 g/cm3, water absorption <0.04%.
Its glass transition temperature is -39°C, brittle temperature is below -62°C, crystal melting point is about 170°C, thermal decomposition temperature is over 316°C and the using temperature range is -40°C~150°C.
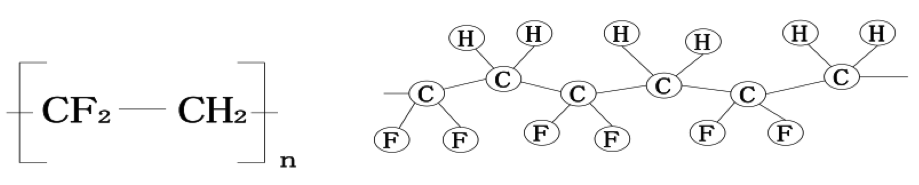
The molecular structure of PVDF is as follows:
The chemical stability and hydrophilia play very important roles in water treatment; chemical stability determines the material’s longevity when it is used in acid-base, oxidizing agents and microorganism, it also directly effects the cleaning methods.
Hydrophilia determines the adsorption degree of material to the organic pollutants in water, which effects the membrane flux.
The main advantages of PVDF is as follows:
- Great chemical stability
The prominent advantage of PVDF is with great chemical stability, it is not easily corroded by acid, alkali, strong oxidant and halogen. The oxidative resistant capacity of PVDF is over 10 times than the material of PES, PS etc.
The PVDF performance remains almost the same when it is under 200~400 nm UV irradiation for a year.
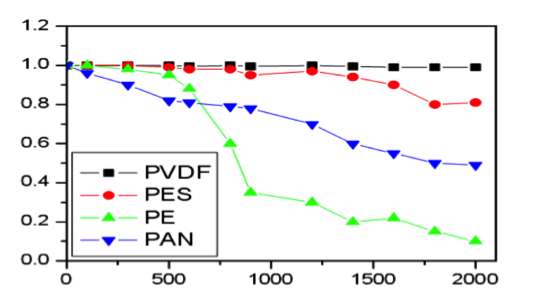
- Anti-pollution
Microorganism and organics are the main reason for irreversible fouling in water treatment, oxidant cleaning is the most effective means to make the flux recovery, at this time, PVDF shows its excellent performance.
- Great toughness
Hollow fiber membrane which is made from PVDF has great toughness and it is not easy to get fatigue damage; the tensile strength of Hollow fiber with PVDF is 500 kg/cm2, it also has great performance of impact strength and wear-resisting.
